オブジェクト指向プログラミングとは? → オブジェクト指向プログラミング - Wikipedia
オブジェクト指向プログラミングでプログラムを書く
円を描くプログラムを、オブジェクト指向プログラミングで書いてみる。
step. 0 これまでの書き方
float x, y, diameter; // x座標, y座標, 直径
void setup() {
x = 25;
y = 50;
diameter = 30;
}
void draw() {
ellipse(x, y, diameter, diameter);
}
step. 1 クラスを定義する
Spot sp; //オブジェクトを宣言
void setup() {
sp = new Spot(); //オブジェクトを生成(構築)
sp.x = 25; //属性(プロパティ)に値を代入。以下同様
sp.y = 50;
sp.diameter = 30;
}
void draw() {
ellipse(sp.x, sp.y, sp.diameter, sp.diameter);
}
//Spotクラスを定義
class Spot {
//属性を定義
float x, y, diameter; // x座標, y座標, 直径
}
※「Spot」は、関数を自分で定義したときのように、適切な名前を考えて付ける。その属性も同様。
step. 2 クラスにメソッド(method)の定義を追加する
Spot sp; //オブジェクトを宣言
void setup() {
sp = new Spot(); //オブジェクトを生成(構築)
sp.x = 25; //属性(プロパティ)に値を代入。以下同様
sp.y = 50;
sp.diameter = 30;
}
void draw() {
sp.display();
}
//Spotクラスを定義
class Spot {
//属性を定義
float x, y, diameter; // x座標, y座標, 直径
//表示するメソッドを定義
void display() {
ellipse(x, y, diameter, diameter);
}
}
step. 3 クラスにコンストラクタ(constructor)の定義を追加する
Spot sp; //オブジェクトを宣言
void setup() {
sp = new Spot(25, 50, 30); //オブジェクトを生成(構築)
}
void draw() {
sp.display();
}
//Spotクラスを定義
class Spot {
//属性を定義
float x, y, diameter; // x座標, y座標, 直径
//コンストラクタを定義
Spot(float _x, float _y, float _diameter) {
x = _x;
y = _y;
diameter = _diameter;
}
//表示するメソッドを定義
void display() {
ellipse(x, y, diameter, diameter);
}
}
step. 4 クラスに移動のメソッドを追加し、アニメーションにする
Spot sp; //オブジェクトを宣言
void setup() {
sp = new Spot(25, 50, 30, 1); //オブジェクトを生成(構築)
}
void draw() {
background(204);
sp.move();
sp.display();
}
//Spotクラスを定義
class Spot {
//属性を定義
float x, y, diameter, speed; // x座標, y座標, 直径, 速さ
//コンストラクタを定義
Spot(float _x, float _y, float _diameter, float _speed) {
x = _x;
y = _y;
diameter = _diameter;
speed = _speed;
}
//移動するメソッドを定義
void move() {
x += speed;
if (x > width + diameter/2) x = -diameter/2;
}
//表示するメソッドを定義
void display() {
ellipse(x, y, diameter, diameter);
}
}
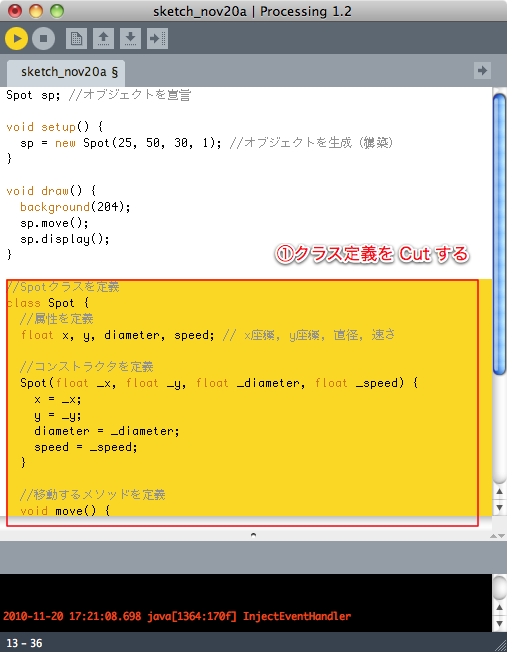
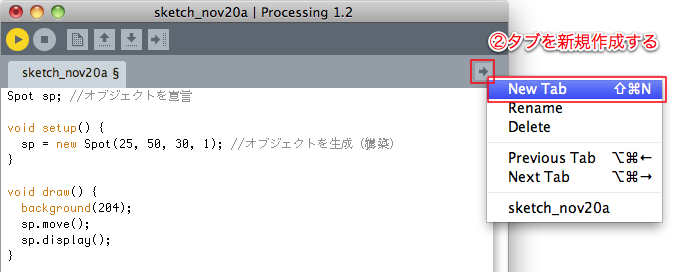
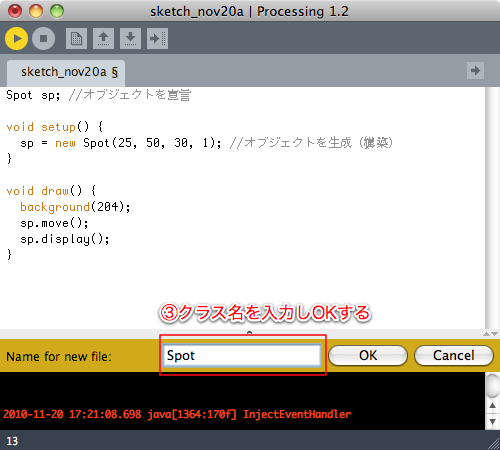
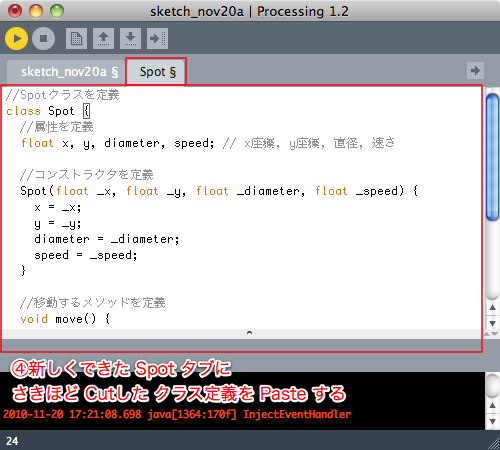
クラス定義を別ファイルで管理する
※以降、Spot.pde ファイルの内容は同じなので省略する
異なる属性を持つ複数のオブジェクトを生成(インスタンス化)する
2個
Spot sp1, sp2; //オブジェクトを宣言
void setup() {
sp1 = new Spot(25, 50, 30, 1); //sp1 を生成
sp2 = new Spot(75, 80, 10, 2); //sp2 を生成
}
void draw() {
background(204);
sp1.move();
sp2.move();
sp1.display();
sp2.display();
}
60個(配列を使って)
Spot[] sp = new Spot[60];
void setup() {
for (int i = 0; i < sp.length; i++) {
sp[i] = new Spot(random(width), random(height), random(5,30), random(0.5,3));
}
}
void draw() {
background(204);
for (int i = 0; i < sp.length; i++) {
sp[i].move();
sp[i].display();
}
}
クラスを継承し、拡張された属性または機能を拡張した子クラスを定義する
Spot クラスを継承し、色を指定できる ColorSpot クラスを定義する
ColorSpot[] sp = new ColorSpot[60];
void setup() {
colorMode(HSB);
for (int i = 0; i < sp.length; i++) {
sp[i] = new ColorSpot(
random(width),
random(height),
random(5,30),
random(0.5,3),
color(random(255), 255, 255)
);
}
}
void draw() {
background(204);
for (int i = 0; i < sp.length; i++) {
sp[i].move();
sp[i].display();
}
}
ColorSpot.pde
//Spotクラスを継承し、ColorSpotクラスを定義
class ColorSpot extends Spot {
//属性を定義
color col; // 色
//コンストラクタを定義
ColorSpot(float _x, float _y, float _diameter, float _speed, color _col) {
super(_x, _y, _diameter, _speed); //親クラス(Spot)のコンストラクタを呼びだす
col = _col;
}
//移動するメソッドを定義
void move() {
super.move(); //親クラス(Spot)のメソッドを呼びだす
}
//表示するメソッドを定義
void display() {
fill(col);
super.display();
}
}
Spot.pde
//Spotクラスを定義
class Spot {
//属性を定義
float x, y, diameter, speed; // x座標, y座標, 直径, 速さ
//コンストラクタを定義
Spot(float _x, float _y, float _diameter, float _speed) {
x = _x;
y = _y;
diameter = _diameter;
speed = _speed;
}
//移動するメソッドを定義
void move() {
x += speed;
if (x > width + diameter/2) x = -diameter/2;
}
//表示するメソッドを定義
void display() {
ellipse(x, y, diameter, diameter);
}
}